Yo, ever wondered what’s the deal with APR on loans? Buckle up, ‘cause we’re about to dive into the nitty-gritty of APR in a way that’ll blow your mind!
So, APR stands for annual percentage rate, and it’s not just about the interest rate, but a whole lot more. Get ready to unravel the mysteries of borrowing money and how APR plays a major role in it.
Importance of Understanding APR on Loans
When it comes to borrowing money, understanding APR (Annual Percentage Rate) is key to making informed financial decisions. Let’s dive into why it’s crucial to grasp the concept of APR and how it can impact your overall borrowing costs.
APR vs. Interest Rate
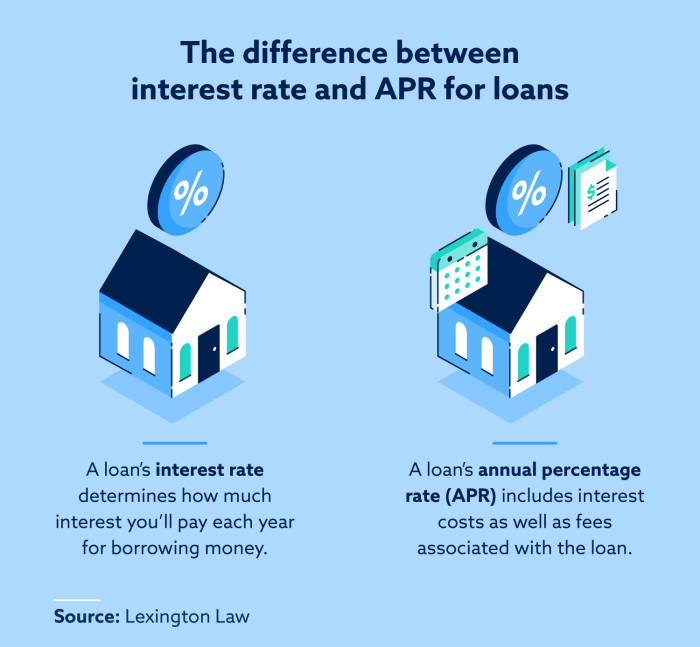
Alright, so APR and interest rate might sound like they’re the same deal, but they’re actually quite different. The interest rate is just the percentage of the loan amount that you’ll pay as interest, while APR includes both the interest rate and any additional fees or charges the lender may tack on. Essentially, APR gives you the total picture of how much the loan is gonna cost you.
Impact on Total Cost
Check it – APR not only affects your monthly payments but also the total amount you’ll end up shelling out over the life of the loan. A higher APR means you’re gonna be forking over more cash in interest and fees, which can seriously add up over time. Understanding APR helps you compare loan offers and choose the one that won’t drain your bank account.
Factors Affecting APR
When it comes to loans, the APR can be influenced by several key factors that borrowers need to be aware of in order to make informed decisions.
Credit Score and Credit History
Your credit score and credit history play a significant role in determining the APR on a loan. Lenders use this information to assess your creditworthiness and determine the level of risk involved in lending to you. Borrowers with higher credit scores and positive credit histories are likely to qualify for lower APRs, while those with lower scores may face higher APRs due to the increased risk.
Loan Term and Loan Amount
The loan term, or the length of time you have to repay the loan, can impact the APR. Generally, loans with longer repayment terms tend to have higher APRs compared to shorter-term loans. This is because lenders take on more risk with longer terms. Additionally, the loan amount can also affect the APR. Larger loan amounts may come with lower APRs, as lenders can spread their costs over a larger loan balance.
Calculating APR
When it comes to loans, understanding the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) is crucial for managing your finances effectively. Calculating APR allows you to determine the true cost of borrowing money, including interest rates and fees. By knowing how to calculate APR, you can make informed decisions about taking out loans and planning your financial future.
Step-by-Step Guide on Calculating APR
To calculate the APR on a loan, follow these steps:
- 1. Determine the total finance charge on the loan, including any fees or additional costs.
- 2. Divide the total finance charge by the loan amount.
- 3. Multiply the result by the number of days in a year (usually 365).
- 4. Multiply the result by 100 to convert it to a percentage.
APR = (Total Finance Charge / Loan Amount) x (365 / Number of Days in Term) x 100
Examples of Different Loan Terms Affecting APR Calculation
- 1. A shorter loan term typically results in a higher APR, as the interest rate is spread over a shorter period.
- 2. Loans with lower fees and lower interest rates will have a lower APR compared to loans with higher fees and interest rates.
- 3. Variable interest rates can lead to fluctuations in APR, making it important to understand the potential impact on your payments.
Significance of Knowing How to Calculate APR for Financial Planning
- 1. Helps you compare loan offers from different lenders to choose the most cost-effective option.
- 2. Allows you to budget and plan for loan payments accurately by understanding the total cost of borrowing.
- 3. Empowers you to make informed financial decisions and avoid taking on debt that may be more expensive in the long run.
Comparing Loans Based on APR
When it comes to borrowing money, looking at the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) is crucial for making informed financial decisions. The APR includes not only the interest rate but also any additional fees or charges associated with the loan. This provides a more accurate representation of the total cost of borrowing.
Comparison Table of Different Loans with Varying APRs
| Loan Type | Interest Rate | Additional Fees | APR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Loan A | 5% | $100 | 5.5% |
| Car Loan B | 3.5% | $500 | 4% |
| Student Loan C | 4.2% | $50 | 4.5% |
Understanding APR allows borrowers to compare loans more effectively. While Loan A may have a lower interest rate, the additional fees result in a higher APR compared to Loan B with a slightly higher interest rate but lower fees. This makes it easier to see which loan offers the best overall value.
