Hey there, ready to dive into the world of mortgage loans? Get ready to learn all about the ins and outs of different types of mortgage loans in this guide that’s gonna blow your mind!
Let’s break down everything you need to know about fixed-rate mortgages, adjustable-rate mortgages, government-backed mortgages, and jumbo loans.
Overview of Mortgage Loans
Mortgage loans are basically loans taken out to buy a home or real estate property. It’s like borrowing money from a bank or lender to purchase your dream house.
Definition of Mortgage Loans
Mortgage loans are a type of loan specifically used for buying a home or property. The borrower agrees to repay the loan amount plus interest over a set period of time.
Purpose of Mortgage Loans
The main purpose of mortgage loans is to enable individuals to become homeowners without having to pay the full purchase price upfront. Instead, they can make monthly payments over time.
Importance of Understanding Different Types of Mortgage Loans
It’s crucial to understand the different types of mortgage loans available because each type has its own terms, interest rates, and repayment options. By knowing your options, you can choose the best mortgage loan that suits your financial situation and goals.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
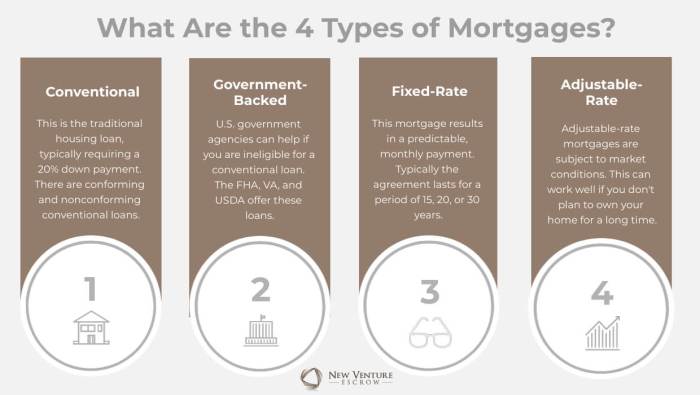
Fixed-rate mortgages are a type of home loan where the interest rate remains the same throughout the entire term of the loan. This means that your monthly payments will also remain constant, providing predictability and stability in budgeting.
How Fixed-Rate Mortgages Work
Fixed-rate mortgages work by setting an interest rate at the beginning of the loan term, which stays fixed for the entire duration of the loan. This means that even if market interest rates rise or fall, your mortgage rate remains unchanged.
- Pros of Fixed-Rate Mortgages:
- Stability: Your monthly payments remain the same, making budgeting easier.
- Predictability: You know exactly how much you need to pay each month.
- Protection: If interest rates rise, you are shielded from increased payments.
- Cons of Fixed-Rate Mortgages:
- Potentially Higher Initial Rates: Fixed-rate mortgages may have higher initial interest rates compared to adjustable-rate mortgages.
- Less Flexibility: If market rates drop significantly, you won’t benefit from lower rates unless you refinance.
- Longer Commitment: Fixed-rate mortgages often come with longer terms, tying you to the same rate for a longer period.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARM)
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages, also known as ARMs, are home loans where the interest rate can change periodically, usually based on an index. This means that your monthly payments can go up or down over time.
Definition and Differences from Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages differ from Fixed-Rate Mortgages in that the interest rate on an ARM can change after a certain period, while the rate on a Fixed-Rate Mortgage remains the same throughout the life of the loan. ARMs often start with lower initial interest rates compared to fixed-rate loans, making them attractive to some borrowers. However, the uncertainty of future rate adjustments can pose risks.
- ARMs typically have an initial fixed-rate period, after which the rate can adjust annually or even monthly.
- When the interest rate changes, your monthly payment will also change, making budgeting more challenging.
- ARMs have caps to limit how much the interest rate can increase or decrease during each adjustment period and over the life of the loan.
It’s essential to understand the terms of an ARM, including how often the rate can adjust, the index it’s tied to, and the caps in place to protect you from extreme rate changes.
Factors Influencing ARM Interest Rate Changes
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages are influenced by various factors that determine how and when the interest rate can change. These factors can include:
- The index: ARMs are tied to specific indexes, such as the LIBOR or the Treasury Index. Changes in these indexes will impact your ARM rate.
- Margins: Lenders add a margin to the index rate to determine your actual interest rate. This margin remains constant throughout the life of the loan.
- Adjustment frequency: The frequency at which your rate can adjust, whether annually, bi-annually, or monthly, will affect the stability of your payments.
- Caps: ARMs have caps that limit how much your interest rate can increase or decrease at each adjustment period and over the life of the loan.
Government-Backed Mortgages
Government-backed mortgages are loans that are supported by the federal government through agencies like the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). These types of loans are designed to make homeownership more accessible to individuals who may not qualify for a conventional mortgage due to various reasons.
FHA Loans
FHA loans are popular among first-time homebuyers and individuals with less-than-perfect credit scores. The eligibility criteria for FHA loans are relatively lenient compared to conventional loans, making them a great option for those who may not have a large down payment or stellar credit history. Borrowers need to have a minimum credit score of 580 to qualify for the low down payment option of 3.5%.
VA Loans
VA loans are exclusively available to active-duty service members, veterans, and eligible surviving spouses. These loans offer competitive interest rates and do not require a down payment or private mortgage insurance (PMI). To be eligible for a VA loan, individuals must meet specific service requirements based on their military status.
USDA Loans
USDA loans are aimed at individuals looking to purchase homes in rural areas. These loans offer low-interest rates and do not require a down payment. To qualify for a USDA loan, borrowers must meet income eligibility requirements and the property must be located in a designated rural area according to USDA guidelines.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Government-Backed Mortgages
- Benefits:
- Lower down payment requirements
- More lenient credit score requirements
- Competitive interest rates
- Flexible eligibility criteria
- Drawbacks:
- Additional fees such as PMI or funding fees
- Property location restrictions for USDA loans
- Potential longer processing times
- Limits on loan amounts
Jumbo Loans
When it comes to buying a really expensive house, regular mortgages might not cut it. That’s where jumbo loans come in. These bad boys are for those looking to borrow more than the conventional loan limits.
Jumbo loans are like the big brother of mortgages. They are designed for high-priced properties that exceed the loan limits set by government-sponsored enterprises like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. So, if you’re eyeing that mansion on the hill, you might need a jumbo loan to make it happen.
Differences between Jumbo Loans and Conventional Loans
Alright, let’s break it down. Conventional loans have limits set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, while jumbo loans have no such boundaries. Jumbo loans usually come with higher interest rates and require a larger down payment. Lenders also tend to scrutinize jumbo loan applicants more closely because of the higher risk involved.
Eligibility Requirements for Jumbo Loans
So, you wanna play in the big leagues with a jumbo loan? You better bring your A-game. To qualify for a jumbo loan, you typically need a stellar credit score (think 700 or higher), a low debt-to-income ratio, and a significant amount of cash reserves. Lenders want to see that you’re financially stable and can handle the hefty payments that come with a jumbo loan.
