So, you wanna know about variable interest rate loans, huh? Well, buckle up because we’re diving into the nitty-gritty of how these loans work and what makes them tick. Get ready for a wild ride through the world of fluctuating interest rates!
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about variable interest rate loans, from the basics to the risks and rewards. Let’s get this show on the road!
Introduction to Variable Interest Rate Loans
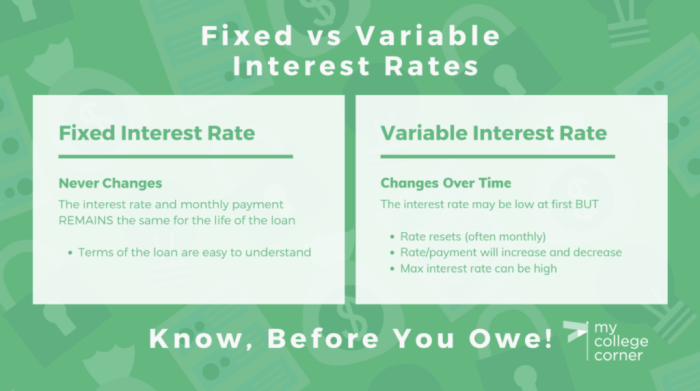
Variable interest rate loans are loans where the interest rate can change over time based on market conditions. Unlike fixed-rate loans where the interest rate remains the same for the entire loan term, variable rates can fluctuate, leading to changes in monthly payments.
Difference Between Variable and Fixed Rates
Variable interest rates differ from fixed rates in that they are not locked in for the duration of the loan. While fixed rates provide stability and predictability in payments, variable rates offer the potential for lower initial rates but come with the risk of rates increasing in the future.
Factors Influencing Variable Interest Rates
- Economic conditions: Factors such as inflation, economic growth, and unemployment rates can impact variable interest rates.
- Market trends: Changes in the overall interest rate environment can cause variable rates to rise or fall.
- Lender policies: Lenders may adjust variable rates based on their own financial considerations and risk assessments.
- Index fluctuations: Variable rates are often tied to an index, such as the prime rate or LIBOR, which can influence rate changes.
Pros and Cons of Variable Interest Rate Loans
When it comes to variable interest rate loans, there are both advantages and disadvantages to consider.
Advantages of Variable Interest Rate Loans
- Flexibility: Variable rate loans can offer lower initial interest rates compared to fixed-rate loans, allowing borrowers to benefit from potential savings.
- Potential Savings: If interest rates decrease, borrowers with variable rate loans can enjoy lower monthly payments and overall interest costs.
- Shorter Loan Terms: Variable rate loans may allow borrowers to pay off their loans faster if interest rates remain low, saving money on interest in the long run.
Disadvantages of Variable Interest Rate Loans
- Uncertainty: The main drawback of variable rate loans is the uncertainty of future interest rate changes, which can lead to higher monthly payments and increased overall costs.
- Risk of Rate Increases: If interest rates rise, borrowers with variable rate loans may face higher monthly payments, potentially causing financial strain.
- Budgeting Challenges: Variable rate loans can make it difficult for borrowers to budget and plan for future payments due to the unpredictable nature of interest rate changes.
Examples of Situations
In situations where interest rates are expected to remain low or decrease, variable rate loans can be beneficial for borrowers looking to take advantage of lower initial rates and potential savings. However, in times of economic uncertainty or rising interest rates, variable rate loans can pose a risk to borrowers who may struggle with higher payments and increased costs.
Factors Influencing Variable Interest Rates
Variable interest rates are not set in stone and can fluctuate based on various factors. Understanding these influences can help borrowers make informed decisions. Let’s delve into how economic indicators, market trends, and financial institutions play a role in determining variable interest rates.
Economic Indicators Impact
Economic indicators such as inflation rates, GDP growth, and unemployment figures can significantly impact variable interest rates. For example, if inflation rises, central banks may increase interest rates to curb inflation. This can cause variable interest rates to go up as well, making borrowing more expensive for consumers.
Market Trends Influence
Market trends, including supply and demand for credit, can also affect variable interest rates. In times of economic uncertainty, lenders may increase interest rates to mitigate risks associated with lending. On the other hand, during periods of economic growth, lenders may lower rates to attract more borrowers.
Role of Financial Institutions
Financial institutions, such as banks and credit unions, ultimately determine the specific variable interest rates offered to borrowers. These institutions take into account various factors, including their cost of funds, operational expenses, and desired profit margins when setting interest rates. Additionally, competition among lenders can impact the rates they offer to remain competitive in the market.
Managing Risks Associated with Variable Interest Rate Loans
When it comes to variable interest rate loans, managing risks is crucial to avoid financial pitfalls. Here are some strategies to help borrowers navigate the uncertainties of fluctuating interest rates.
Options for Refinancing Variable Interest Rate Loans
Refinancing a variable interest rate loan can be a smart move to lock in a lower rate or switch to a fixed-rate loan. Here are some options to consider:
- Shop around for competitive rates from different lenders.
- Consult with a financial advisor to analyze the potential savings of refinancing.
- Consider the costs associated with refinancing, such as closing fees and prepayment penalties.
Tips for Borrowers to Navigate Potential Interest Rate Hikes
Interest rate hikes can significantly impact variable rate loans, leading to higher monthly payments. Here are some tips to help borrowers manage potential rate increases:
- Monitor the market trends and economic indicators that influence interest rates.
- Build a financial cushion to prepare for higher payments in case of rate hikes.
- Consider making extra payments towards the principal to reduce the impact of rate increases.
