Yo, diving into asset allocation strategies is like unlocking the secrets to making your money work for you. We’re about to break it down in a way that’s totally lit and easy to understand.
So, let’s get ready to learn about the different types, factors influencing decisions, and how to actually implement these strategies for maximum gains. Get ready to level up your investment game!
Overview of Asset Allocation Strategies
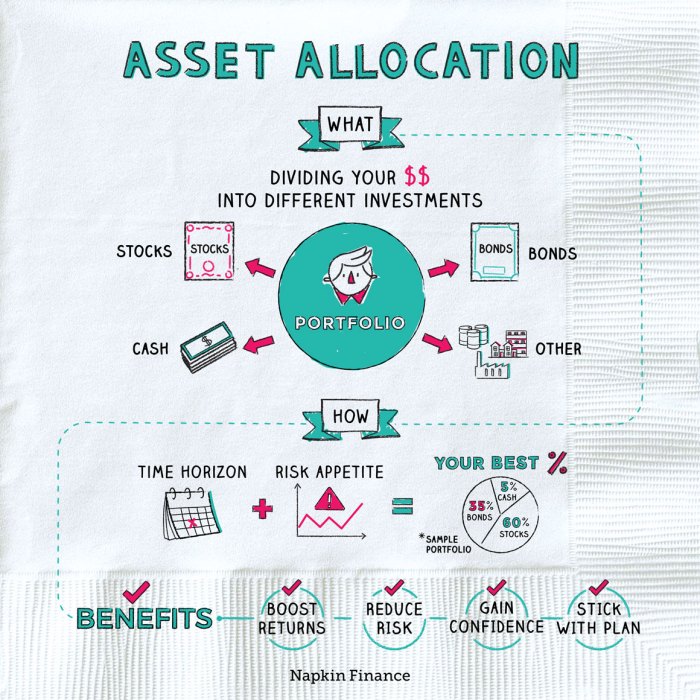
Asset allocation strategies are crucial in the world of investing. They involve dividing your investment portfolio among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. The main goal of asset allocation strategies is to balance risk and return based on your financial goals and risk tolerance. By diversifying your investments, you can reduce the impact of market volatility on your portfolio while maximizing potential returns.
Primary Goals of Asset Allocation Strategies
- Minimize Risk: Asset allocation helps spread risk across different asset classes, reducing the impact of a downturn in any single investment.
- Maximize Returns: By allocating investments strategically, you can aim to achieve the highest possible return given your risk tolerance.
- Align with Financial Goals: Asset allocation allows you to tailor your investment mix to align with your financial objectives, whether it’s saving for retirement, buying a house, or funding education.
How Asset Allocation Strategies Manage Risk and Maximize Returns
- Portfolio Diversification: By spreading investments across various asset classes, industries, and regions, asset allocation reduces the impact of market fluctuations on your overall portfolio.
- Rebalancing: Regularly reviewing and rebalancing your portfolio ensures that it stays aligned with your investment goals and risk tolerance, helping to maximize returns over the long term.
- Risk Assessment: Asset allocation strategies involve evaluating your risk tolerance to determine the right mix of investments that will help you achieve your financial objectives without taking on unnecessary risk.
Types of Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation strategies are crucial for investors to achieve their financial goals and manage risk effectively. There are several types of asset allocation strategies commonly used in the investment world. Let’s delve into the details of these strategies and understand how they differ from each other.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation involves setting a target mix of asset classes and sticking to it for the long term. This strategy aims to achieve a balance between risk and return based on the investor’s financial goals and risk tolerance. An example of a strategic asset allocation model is the 60/40 portfolio, where 60% is allocated to stocks and 40% to bonds.
Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation involves making short-term adjustments to the asset allocation based on market conditions or economic outlook. This strategy allows investors to capitalize on short-term opportunities or mitigate risks. An example of a tactical asset allocation model is market timing, where investors adjust their allocation based on market trends.
Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation combines elements of both strategic and tactical asset allocation. It involves adjusting the asset allocation based on predefined rules or quantitative models. This strategy aims to capture market opportunities while managing risk effectively. An example of dynamic asset allocation is a risk parity strategy, where assets are allocated based on risk rather than traditional market capitalization.
Passive vs. Active Asset Allocation Strategies
Passive asset allocation strategies involve maintaining a static portfolio based on the initial asset allocation without making frequent changes. These strategies typically follow a buy-and-hold approach and aim to minimize trading costs. On the other hand, active asset allocation strategies involve frequent adjustments to the portfolio based on market conditions or investment outlook. Active strategies seek to outperform the market through active management.
In conclusion, asset allocation strategies play a crucial role in shaping an investor’s portfolio and achieving long-term financial success. By understanding the different types of asset allocation strategies and their characteristics, investors can make informed decisions that align with their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Factors Influencing Asset Allocation
When it comes to asset allocation decisions, several key factors play a crucial role in determining the most suitable investment strategy. Factors such as risk tolerance, investment goals, time horizon, economic conditions, and market trends all influence how investors allocate their assets.
Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance refers to an individual’s ability to withstand fluctuations in the value of their investments. It plays a significant role in asset allocation decisions as investors with a higher risk tolerance may be more inclined to allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to higher-risk assets such as stocks. On the other hand, investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer a more conservative approach, allocating a higher percentage of their portfolio to lower-risk assets like bonds.
Investment Goals
Investment goals are another crucial factor that influences asset allocation decisions. Whether an investor is looking to generate income, preserve capital, or achieve long-term growth will impact the allocation of assets in their portfolio. For example, an investor with a goal of generating income may allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to dividend-paying stocks or bonds, while an investor seeking growth may focus more on equities.
Time Horizon
The time horizon, or the length of time an investor plans to hold onto their investments, is a key factor in determining asset allocation. Investors with a longer time horizon may be able to take on more risk in their portfolio as they have more time to recover from market downturns. On the other hand, investors with a shorter time horizon may opt for a more conservative approach to protect their capital.
Economic Conditions and Market Trends
Economic conditions and market trends also play a significant role in influencing asset allocation strategies. During times of economic uncertainty or market volatility, investors may choose to adjust their asset allocation to reduce risk exposure. For example, in a bear market, investors may shift towards safer assets like bonds or cash to preserve capital.
Implementation of Asset Allocation Strategies
When it comes to implementing asset allocation strategies, there are a few key steps to keep in mind. It’s important to select appropriate asset classes for a diversified portfolio and have a plan for rebalancing to maintain target asset allocations over time.
Selecting Appropriate Asset Classes
- Consider your investment goals and risk tolerance when choosing asset classes.
- Diversify across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
- Research historical performance and correlation between asset classes to make informed decisions.
- Consult with a financial advisor to ensure your portfolio aligns with your long-term objectives.
Rebalancing Techniques
- Regularly review your portfolio to see if it’s deviated from your target asset allocations.
- Rebalance by selling overperforming assets and buying underperforming ones to bring your portfolio back in line.
- Set specific triggers or thresholds for rebalancing to avoid emotional decision-making.
- Consider tax implications when rebalancing and strategize accordingly.
