Yo, so capital gains tax is about to take center stage, giving you the lowdown on a topic that’s got all the deets you need. Get ready for a deep dive into the world of taxes, with a twist of cool and a side of savvy slang.
Now, let’s break it down and serve up some fresh info on this whole capital gains tax deal.
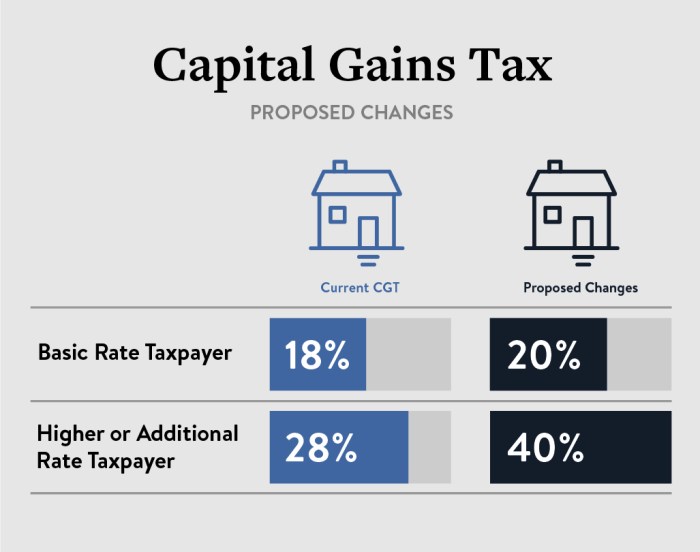
Overview of Capital Gains Tax
Capital gains tax is a type of tax imposed on the profit made from the sale of an asset or investment. It is different from other taxes like income tax because it specifically targets the increase in value of certain assets over time.
The purpose of imposing capital gains tax is to ensure that individuals or businesses pay taxes on the gains they make from investments, rather than just on their regular income. This helps to promote fairness in the tax system and ensures that those who benefit from asset appreciation contribute to government revenue.
Assets Subject to Capital Gains Tax
- Stocks and bonds
- Real estate properties
- Precious metals
- Collectibles like art and antiques
Calculation of Capital Gains Tax
When it comes to calculating capital gains tax, it’s important to understand the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains tax rates. The basic concept is that capital gains tax is the tax you pay on the profit you make from selling an asset like stocks, real estate, or other investments. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Capital Gains Tax Rates
Short-term capital gains tax rates are applied to assets that are held for one year or less before being sold. These are taxed at ordinary income tax rates, which can range from 10% to 37% depending on your total income for the year.
On the other hand, long-term capital gains tax rates are applied to assets that are held for more than one year before being sold. These rates are typically lower than short-term rates and can range from 0% to 20%, again depending on your income level.
Deductions and Exemptions
There are some deductions and exemptions that may apply to capital gains tax. For example, if you sell your primary residence, you may be able to exclude up to $250,000 of capital gains from taxation ($500,000 for married couples filing jointly). Additionally, if you reinvest your capital gains into a Qualified Opportunity Fund, you may be able to defer or reduce your tax liability.
Understanding how capital gains tax is calculated and taking advantage of any deductions or exemptions can help you minimize the amount of tax you owe on your investment profits.
Impact of Capital Gains Tax
When it comes to the impact of capital gains tax, there are several key factors to consider. Let’s dive into how this tax can affect investment decisions, the stock market, and individuals’ financial obligations.
Investment Decisions
Capital gains tax can significantly influence investment decisions. When investors know they will be taxed on their profits, they may be more hesitant to sell their assets, as they will have to pay a percentage of their gains to the government. This can lead to a decrease in trading activity and potentially impact market liquidity.
Economic Implications on Stock Market
The capital gains tax can have a direct impact on the stock market. High capital gains taxes can discourage investors from buying and selling stocks, which can lead to decreased market activity and volatility. Additionally, changes in capital gains tax rates can influence investor behavior and overall market sentiment.
Scenarios of Significant Tax Obligations
Individuals may face significant capital gains tax obligations in various scenarios. For example, if someone sells a property or stocks that have appreciated significantly over time, they may incur a substantial tax bill. This can impact their overall financial planning and decision-making process, as they will need to account for the tax implications of their investment choices.
Strategies to Minimize Capital Gains Tax
When it comes to minimizing capital gains tax, there are several smart strategies that individuals can use to lower their tax liability and keep more of their investment gains. By understanding these strategies, investors can make informed decisions to optimize their tax situation.
Comparing Tax-Deferred vs. Taxable Investment Accounts
- One effective strategy is to utilize tax-deferred investment accounts such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans. Contributions to these accounts are made with pre-tax dollars, allowing investments to grow tax-free until withdrawals are made in retirement. This can help defer capital gains taxes and potentially reduce overall tax burden.
- In contrast, taxable investment accounts are subject to capital gains taxes on any profits realized when assets are sold. However, these accounts offer more flexibility in terms of investment choices and withdrawal options compared to tax-deferred accounts.
Timing of Asset Sales
- Another key strategy is to carefully time the sale of assets to optimize capital gains tax obligations. By holding investments for more than a year before selling, individuals can qualify for the lower long-term capital gains tax rates, which are typically more favorable than short-term capital gains tax rates. This can result in significant tax savings over time.
- On the other hand, selling investments at a loss can also be strategically beneficial as capital losses can be used to offset capital gains, reducing overall tax liability. This strategy, known as tax-loss harvesting, can help investors minimize the impact of capital gains taxes on their investment returns.
