Yo, peeps! Let’s dive into the world of credit card interest explained. Get ready for a rollercoaster ride through the ins and outs of how those sneaky interest rates work. It’s gonna be lit!
So, buckle up and prepare to level up your knowledge on credit card interest like a boss.
Understanding Credit Card Interest
Credit card interest is basically the extra amount of money you have to pay on top of the purchases you make using your credit card. It’s like a fee for borrowing money from the credit card company.
When it comes to calculating credit card interest, it’s usually based on the average daily balance of your credit card account. The credit card company multiplies this balance by the daily interest rate and then adds up these daily interest charges over the billing cycle to determine the total interest you owe.
Difference between APR and APY
APR stands for Annual Percentage Rate, which is the annual rate charged for borrowing or earned through an investment, expressed as a percentage. It includes the interest rate and any additional fees charged by the credit card company.
APY, on the other hand, stands for Annual Percentage Yield. It takes into account the effect of compound interest, which means you earn interest on both your initial deposit and any interest already earned. APY gives a more accurate picture of how much you’ll actually earn or owe over time compared to APR.
Factors Influencing Credit Card Interest Rates
When it comes to credit card interest rates, there are several factors that can influence how much you end up paying. Understanding these factors can help you make better financial decisions and save money in the long run.
Credit Card Companies’ Risk Assessment
Credit card companies determine interest rates based on their assessment of the risk associated with lending to a particular customer. Factors such as credit history, credit score, income level, and existing debt play a crucial role in this evaluation. Customers with a lower credit score or a history of missed payments are considered higher risk and may be charged a higher interest rate to compensate for the increased likelihood of default.
Credit History and Credit Score Impact
Your credit history and credit score have a significant impact on the interest rates you are offered by credit card companies. A good credit score indicates to lenders that you are a responsible borrower who is likely to repay debts on time. As a result, individuals with high credit scores are more likely to qualify for lower interest rates compared to those with poor credit scores. Maintaining a positive credit history by making timely payments and keeping debt levels low can help you secure better interest rates on credit cards.
Types of Credit Card Interest
When it comes to credit card interest rates, there are two main types: fixed and variable. Each type has its own set of pros and cons that borrowers should consider before choosing a credit card.
Fixed Interest Rates
- Fixed interest rates remain the same throughout the life of the credit card.
- Pros: Borrowers have predictable monthly payments and don’t have to worry about fluctuations in interest rates.
- Cons: If market interest rates drop, borrowers with fixed rates won’t benefit from lower rates.
Variable Interest Rates
- Variable interest rates can change periodically based on an underlying interest rate index.
- Pros: Borrowers can benefit from lower interest rates if market rates decrease.
- Cons: Monthly payments can fluctuate, making it harder to budget for payments.
Introductory 0% APR Offers
- Introductory 0% APR offers allow borrowers to pay no interest for a set period, usually 12 to 18 months.
- During the introductory period, borrowers can save money on interest charges and pay down their balance faster.
- However, it’s important to note that once the introductory period ends, the interest rate will revert to the regular rate, which can be high.
Managing Credit Card Interest
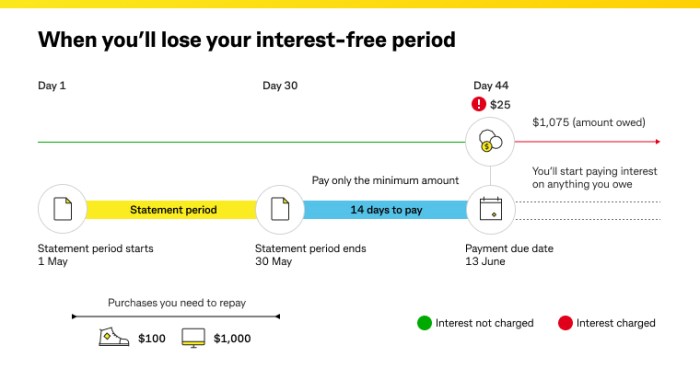
When it comes to managing credit card interest, there are a few key strategies to keep in mind to avoid getting hit with high charges and paying off debt efficiently.
Avoiding High Credit Card Interest Charges
- Always pay your credit card bill on time to avoid late fees and penalty interest rates.
- Avoid carrying a balance on your credit card whenever possible to prevent interest from accruing.
- Consider setting up automatic payments to ensure you never miss a payment deadline.
- Monitor your credit card statements regularly to catch any errors or unauthorized charges that could increase your balance.
Paying Off Credit Card Debt Efficiently
- Focus on paying off high-interest credit card debt first to minimize the total amount of interest you’ll end up paying.
- Consider using a balance transfer to move high-interest debt to a card with a lower interest rate, if possible.
- Create a budget and prioritize paying more than the minimum payment each month to speed up debt repayment.
- Explore debt consolidation options to combine multiple debts into one lower-interest loan for easier repayment.
Importance of Timely Payments
- Making timely payments is crucial to reducing interest accumulation on your credit card balance over time.
- Avoiding late payments can help maintain or improve your credit score, leading to better interest rates in the future.
- Consistently paying on time shows lenders that you are reliable and responsible with managing your finances.
- Even a single late payment can trigger penalty fees and higher interest rates, so it’s essential to stay on top of due dates.
