Yo, peep this! We’re diving into the world of debt-to-income ratio explained, giving you the lowdown on how this financial metric impacts your moolah. Get ready for a wild ride!
So, let’s break it down – debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is basically a fancy term that shows how much of your income goes towards paying off debts. It’s crucial in understanding your financial health, so pay attention, folks!
Overview of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-Income Ratio, also known as DTI, is a financial metric that compares the amount of debt you owe to your overall income. It is a crucial factor that lenders consider when determining your creditworthiness and ability to repay loans.
What is Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Debt-to-Income Ratio is calculated by dividing your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income. This ratio is usually expressed as a percentage and helps lenders assess your ability to manage additional debt.
- High DTI ratios indicate that you may be overextended and have difficulty making timely payments.
- Low DTI ratios show that you have a good balance between your income and debt obligations.
DTI = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100
Why is DTI Important?
Having a low DTI is crucial when applying for loans or mortgages as it demonstrates your financial stability and ability to manage debt responsibly. Lenders use this ratio to evaluate your risk level and determine whether you can afford additional debt.
How is DTI Calculated?
To calculate your DTI, add up all your monthly debt payments such as credit card bills, student loans, and mortgage payments. Then, divide this total by your gross monthly income, which includes salary, bonuses, and other sources of income.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI) plays a crucial role in financial planning as it gives a clear picture of an individual’s financial health and their ability to manage debt responsibly.
Significance of DTI in Financial Planning
DTI helps individuals understand how much of their income goes towards debt payments, indicating their level of financial obligation. A lower DTI ratio typically signifies better financial health and a higher likelihood of being approved for loans or credit.
How Lenders Use DTI in Loan Applications
- Lenders use DTI to assess a borrower’s ability to repay a loan by comparing their total monthly debt payments to their gross monthly income.
- A lower DTI ratio indicates that a borrower has more disposable income to cover new loan payments, making them less risky for lenders.
- Most lenders have specific DTI requirements for different types of loans, such as mortgages, auto loans, and personal loans.
Impact of DTI on Financial Health
A high DTI ratio suggests that an individual is heavily burdened by debt and may struggle to make timely payments, potentially leading to financial distress and a negative impact on credit scores.
By maintaining a healthy DTI ratio, individuals can better manage their finances, qualify for better loan terms, and improve their overall financial well-being in the long run.
Types of Debt-to-Income Ratios
When it comes to debt-to-income ratios, there are two main types that lenders consider: front-end and back-end DTI ratios. These ratios help assess an individual’s ability to manage their debt payments in relation to their income.
Front-End DTI Ratio
The front-end DTI ratio focuses solely on housing-related expenses compared to gross monthly income. To calculate the front-end DTI ratio, you need to add up all housing-related expenses, such as mortgage payments, property taxes, homeowner’s insurance, and HOA fees, and divide that total by your gross monthly income. The result is then multiplied by 100 to get a percentage.
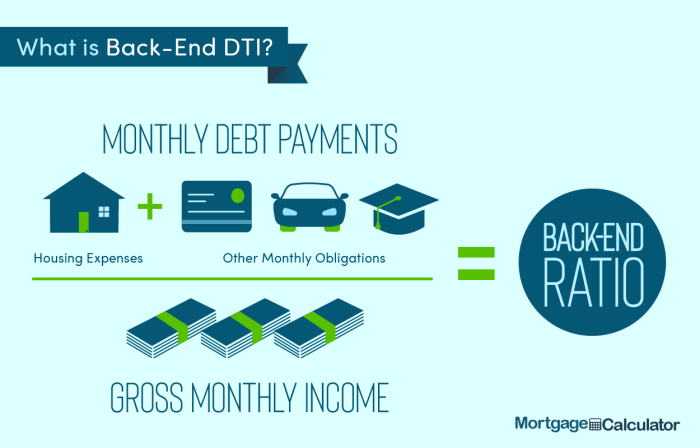
Back-End DTI Ratio
On the other hand, the back-end DTI ratio looks at all debt obligations, including housing expenses, compared to gross monthly income. To calculate the back-end DTI ratio, you need to add up all monthly debt payments like credit card bills, student loans, car loans, and personal loans, in addition to housing expenses. Divide this total by your gross monthly income and multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
Ideal Debt-to-Income Ratio
When it comes to your debt-to-income ratio (DTI), the lower, the better! A good DTI ratio is typically around 36% or lower, meaning that your total monthly debt payments should not exceed 36% of your gross monthly income.
Comparing Ideal DTI Ratios for Different Financial Goals
- Buying a Home: For buying a home, lenders often look for a DTI ratio of 28% or lower. This shows that you have a good balance between your income and debt, making you a less risky borrower.
- Qualifying for a Loan: When qualifying for a loan, especially a mortgage, a lower DTI ratio can increase your chances of approval. Lenders want to see that you have enough income to comfortably handle your current debts along with any new loan payments.
Tips to Improve Your DTI Ratio
- Avoid taking on new debt: Try not to add any new loans or credit card balances that could increase your DTI ratio.
- Increase your income: Consider options like getting a part-time job or freelancing to boost your income and lower your DTI ratio.
- Pay off existing debt: Focus on paying off high-interest debts first to reduce your monthly payments and improve your DTI ratio.
