Yo, get ready to dive into the world of dividend payout ratios! This topic is all about the cash companies shell out to their shareholders, and we’re about to break it down in a way that’s easy to understand. So, buckle up and let’s get this party started!
Alright, so let’s kick things off by talking about what dividend payout ratios actually are and why they matter so much in the finance game.
Definition of Dividend Payout Ratios
Dividend payout ratios are a financial metric used to measure the percentage of earnings that a company distributes to its shareholders in the form of dividends. It indicates how much of the company’s profits are being returned to shareholders versus how much is being retained for growth or other purposes.
Calculation of Dividend Payout Ratios
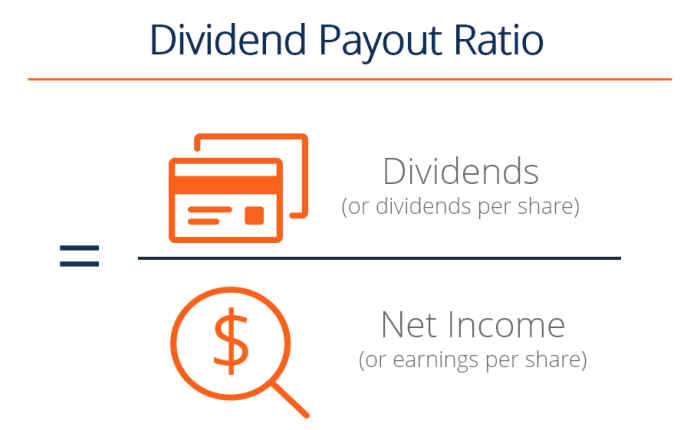
To calculate the dividend payout ratio, you can use the following formula:
Dividend Payout Ratio = Dividends per Share / Earnings per Share
For example, if a company pays out $2 in dividends per share and has earnings per share of $4, the dividend payout ratio would be 0.5 or 50%.
Significance of Dividend Payout Ratios
– For Investors: Dividend payout ratios can help investors assess the sustainability of dividend payments and the company’s financial health. A high ratio may indicate that the company is returning a significant portion of its profits to shareholders, while a low ratio could suggest potential for future dividend growth.
– For Companies: Companies use dividend payout ratios to determine how much of their earnings they want to distribute to shareholders. It can also signal to investors the company’s confidence in its ability to generate consistent profits.
Importance of Dividend Payout Ratios
When it comes to investing, dividend payout ratios play a crucial role in helping investors make informed decisions about which stocks to buy. These ratios provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health and its ability to sustain and grow dividends over time.
Impact of High vs. Low Dividend Payout Ratios
- High Dividend Payout Ratios: Companies with high dividend payout ratios tend to distribute a larger portion of their earnings as dividends to shareholders. While this may seem attractive to income-seeking investors, it could also indicate that the company is not reinvesting enough in its own growth. High dividend payouts may limit the company’s ability to fund future projects or expand its operations, potentially impacting stock performance in the long run.
- Low Dividend Payout Ratios: On the other hand, companies with low dividend payout ratios retain a larger portion of their earnings to reinvest back into the business. While this may result in lower immediate returns for shareholders, it can lead to higher growth potential and increased stock value over time. Companies with low payout ratios have more financial flexibility to weather economic downturns or invest in new opportunities, making them attractive to investors looking for long-term growth.
Indication of Company’s Financial Health
Dividend payout ratios can serve as a key indicator of a company’s financial health. A stable and consistent dividend payout ratio over time suggests that the company has a healthy balance between rewarding shareholders and retaining earnings for future growth. Fluctuations in the dividend payout ratio may signal changes in the company’s profitability, cash flow, or overall financial performance, prompting investors to reevaluate their investment decisions.
Factors Influencing Dividend Payout Ratios
When it comes to dividend payout ratios, there are several key factors that influence how much a company decides to distribute to its shareholders. Let’s take a closer look at some of these factors.
Company Size and Growth Prospects
Company size and growth prospects play a significant role in determining dividend payout ratios. Smaller companies with limited cash flow may opt to reinvest their earnings back into the business to fuel growth, rather than distributing dividends to shareholders. On the other hand, larger, more established companies with stable earnings and cash flow may choose to pay out a higher percentage of their profits as dividends. This decision is often influenced by the company’s growth prospects and the need to balance rewarding shareholders with reinvesting in future growth opportunities.
Role of Industry Norms and Economic Conditions
Industry norms and economic conditions also play a crucial role in determining dividend payout ratios. Different industries have varying practices when it comes to dividend payments. For example, mature industries with stable cash flows may have higher average payout ratios compared to industries with higher growth potential but more volatile earnings. Additionally, economic conditions such as interest rates, inflation, and overall market stability can impact a company’s ability and willingness to pay dividends. Companies often adjust their dividend policies in response to changes in the economic environment to ensure financial stability and shareholder satisfaction.
Analysis of Dividend Payout Ratios
When analyzing dividend payout ratios, it is essential to understand how much of a company’s earnings are being distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends. This ratio provides insight into the company’s financial health and its ability to sustain dividend payments over time.
Step-by-Step Guide to Analyzing Dividend Payout Ratios
- Calculate the dividend payout ratio by dividing the total dividends paid by the company by its net income.
- Compare the ratio to industry benchmarks to assess how the company’s dividend policy stacks up against competitors.
- Consider historical trends to see if the dividend payout ratio has been increasing, decreasing, or remaining stable over time.
- Analyze the company’s future earnings prospects to determine if the current dividend payout ratio is sustainable.
Illustrating Changes in Earnings Impact on Dividend Payout Ratios
Changes in a company’s earnings can have a significant impact on its dividend payout ratio. For example, if a company’s earnings increase while dividend payments remain constant, the dividend payout ratio will decrease. On the other hand, if earnings decrease and dividends stay the same, the dividend payout ratio will increase.
Implications of Fluctuations in Dividend Payout Ratios for Shareholders
Fluctuations in dividend payout ratios can have important implications for shareholders. A decreasing ratio may signal financial trouble or a shift in the company’s dividend policy, leading to uncertainty among investors. Conversely, an increasing ratio could indicate a stronger financial position or a commitment to returning more profits to shareholders.
