Yo, so you wanna know about financial yield calculation, huh? Well, buckle up because we’re diving into the world of numbers and investments in a way that’s gonna make your head spin – in a good way, of course.
So, picture this – you’re an investor looking to make some serious cash. Understanding financial yield calculation is key to making smart decisions and maximizing your profits. Let’s break it down for you.
Definition and Importance of Financial Yield Calculation
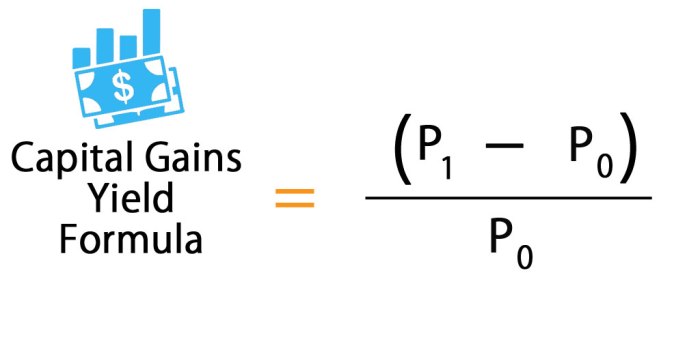
Financial yield calculation is a method used by investors to determine the return on their investment over a specific period of time. It is a crucial tool in evaluating the performance and profitability of an investment.
Why Financial Yield Calculation is Important
Financial yield calculation helps investors make informed decisions by providing a clear picture of the potential return on their investment. By knowing the expected yield, investors can assess the risk and reward associated with a particular investment.
- It allows investors to compare different investment opportunities and choose the one that offers the highest yield.
- Financial yield calculation helps investors set realistic financial goals and track their progress towards achieving them.
- It enables investors to forecast future cash flows and make adjustments to their investment strategy accordingly.
Examples of How Financial Yield Calculation Impacts Investment Decisions
Let’s take a look at how financial yield calculation can influence investment decisions:
- Scenario 1: An investor is considering two investment options – Option A offers a 5% annual yield, while Option B offers a 7% annual yield. By calculating the financial yield, the investor can see that Option B provides a higher return on investment, making it a more attractive choice.
- Scenario 2: A company is planning to invest in a new project. By using financial yield calculation, the company can estimate the potential return on investment and decide whether the project is financially viable.
Types of Financial Yield Calculation Methods
When it comes to calculating financial yield, there are several methods that investors and analysts use to determine the return on their investments. Each method has its own unique approach and is suitable for different types of investments and scenarios.
1. Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is a popular method used by investors to calculate the return on their investment in dividend-paying stocks. It is calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the current share price and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. For example, if a stock pays an annual dividend of $2 per share and the current share price is $50, the dividend yield would be 4% ($2/$50 x 100).
2. Yield to Maturity
Yield to maturity is a method used to calculate the total return an investor can expect to receive from a bond if they hold it until maturity. It takes into account the bond’s current market price, its face value, the coupon rate, and the time to maturity. This calculation gives investors an idea of the annualized return they can expect from the bond.
3. Capital Gains Yield
Capital gains yield is used to calculate the return on an investment solely based on the appreciation of the asset’s price. It is calculated by dividing the change in price of the asset by the original price and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. For example, if you buy a stock for $100 and sell it for $120, the capital gains yield would be 20% (($120-$100)/$100 x 100).
4. Rental Yield
Rental yield is a method used to calculate the return on investment for real estate properties that are rented out. It is calculated by dividing the annual rental income by the property’s value and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. For example, if a property generates $12,000 in annual rental income and is valued at $200,000, the rental yield would be 6% ($12,000/$200,000 x 100).
Factors Affecting Financial Yield Calculation
When it comes to calculating financial yield, there are several key factors that can influence the outcome. These factors can range from internal variables like the initial investment amount to external economic conditions and risk assessments. Understanding how these factors impact financial yield calculations is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Internal Variables
- The initial investment amount: The amount of money you initially invest in a financial asset or project will directly impact the financial yield. A higher initial investment typically results in a higher yield, assuming all other factors remain constant.
- Time period: The length of time for which you hold an investment can significantly affect the financial yield. Longer investment periods may result in higher yields due to compounding interest.
- Interest rates: Fluctuations in interest rates can have a direct impact on financial yield calculations. Higher interest rates generally lead to higher yields, while lower rates may result in lower yields.
External Economic Factors
- Inflation: Inflation rates can erode the real value of returns on investments, affecting the overall financial yield. It is essential to consider inflation when calculating yields to ensure accurate projections.
- Economic conditions: The overall economic environment, including factors like GDP growth, unemployment rates, and market stability, can influence financial yield calculations. Strong economic conditions often lead to higher yields, while economic downturns may result in lower yields.
- Market volatility: Fluctuations in the financial markets can impact the performance of investments, affecting financial yield calculations. It is important to assess market volatility and its potential impact on yields when making investment decisions.
Risk Assessment
- Risk tolerance: Individual risk tolerance levels play a significant role in financial yield calculations. Higher-risk investments may offer the potential for higher yields but also come with increased volatility and the possibility of losses.
- Diversification: Diversifying your investment portfolio can help mitigate risks and improve overall financial yield. By spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and regions, you can reduce the impact of individual asset performance on your overall yield.
- Risk-adjusted return: It is essential to consider the risk-adjusted return of an investment when calculating financial yield. Investments with higher returns may also come with higher levels of risk, and it is crucial to assess whether the potential yield justifies the associated risks.
Application of Financial Yield Calculation in Different Investment Vehicles
Investors use financial yield calculation to assess the return on their investments in various vehicles such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. This calculation helps them make informed decisions about where to allocate their funds based on the expected returns.
Stocks
In stocks, financial yield calculation is commonly known as the dividend yield. This is calculated by dividing the annual dividends per share by the price per share. For example, if a stock pays out $2 in dividends per share and the stock price is $50, the dividend yield would be 4% ($2 / $50 = 0.04 or 4%). Investors often use this metric to compare the dividend-paying ability of different stocks.
Bonds
When it comes to bonds, financial yield calculation is crucial for determining the yield to maturity (YTM). YTM takes into account the bond’s current price, its face value, the coupon rate, and the time remaining until maturity. It provides investors with a more accurate picture of the return they can expect from holding the bond until maturity.
Real Estate Investments
In real estate, financial yield calculation is used to determine the capitalization rate, also known as the cap rate. The cap rate is calculated by dividing the property’s net operating income (NOI) by its current market value. This metric helps investors evaluate the profitability of a real estate investment and compare it to other potential properties.
Overall, adjusting financial yield calculations based on the type of investment is crucial for making sound investment decisions. Each investment vehicle has unique characteristics and factors that influence its yield calculation, so understanding these differences is essential for investors to maximize their returns.
Challenges and Limitations of Financial Yield Calculation
When it comes to calculating financial yield, there are several challenges and limitations that investors and analysts may face. These can impact the accuracy and reliability of the calculations, potentially leading to misguided investment decisions.
Common Challenges Faced in Financial Yield Calculation
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in financial markets can make it challenging to predict future returns accurately.
- Data Accuracy: Obtaining precise and up-to-date financial data is crucial for accurate yield calculations, but this can be difficult due to various factors.
- Complex Investment Structures: Some investment vehicles have intricate structures that make it challenging to determine the correct yield.
Limitations of Financial Yield Calculation Methods
- Assumption-Based Calculations: Many yield calculation methods rely on assumptions that may not always hold true in real-world scenarios, leading to inaccuracies.
- Ignoring External Factors: Some yield calculation methods fail to consider external factors such as economic conditions, regulatory changes, and geopolitical events that can impact investment returns.
- Historical Data Limitations: Using historical data to predict future yields may not always be reliable, especially in rapidly changing market environments.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges and Limitations
- Regularly Update Data: Stay informed with the latest financial data and adjust calculations accordingly to improve accuracy.
- Use Sensitivity Analysis: Conduct sensitivity analysis to assess the impact of different variables on yield calculations and account for uncertainties.
- Consult with Experts: Seek advice from financial experts or analysts to navigate complex investment structures and ensure accurate yield calculations.
