Yo, we’re diving deep into fixed vs variable loan rates, giving you the lowdown on these money matters with a twist of American teen slang style. Get ready to learn all about the differences and factors you gotta consider when choosing the right rates for you.
In this guide, we’ll break down the concept of fixed and variable rates, compare their pros and cons, and explore the risks and market trends associated with each. So, buckle up and let’s roll!
Differences between fixed and variable loan rates
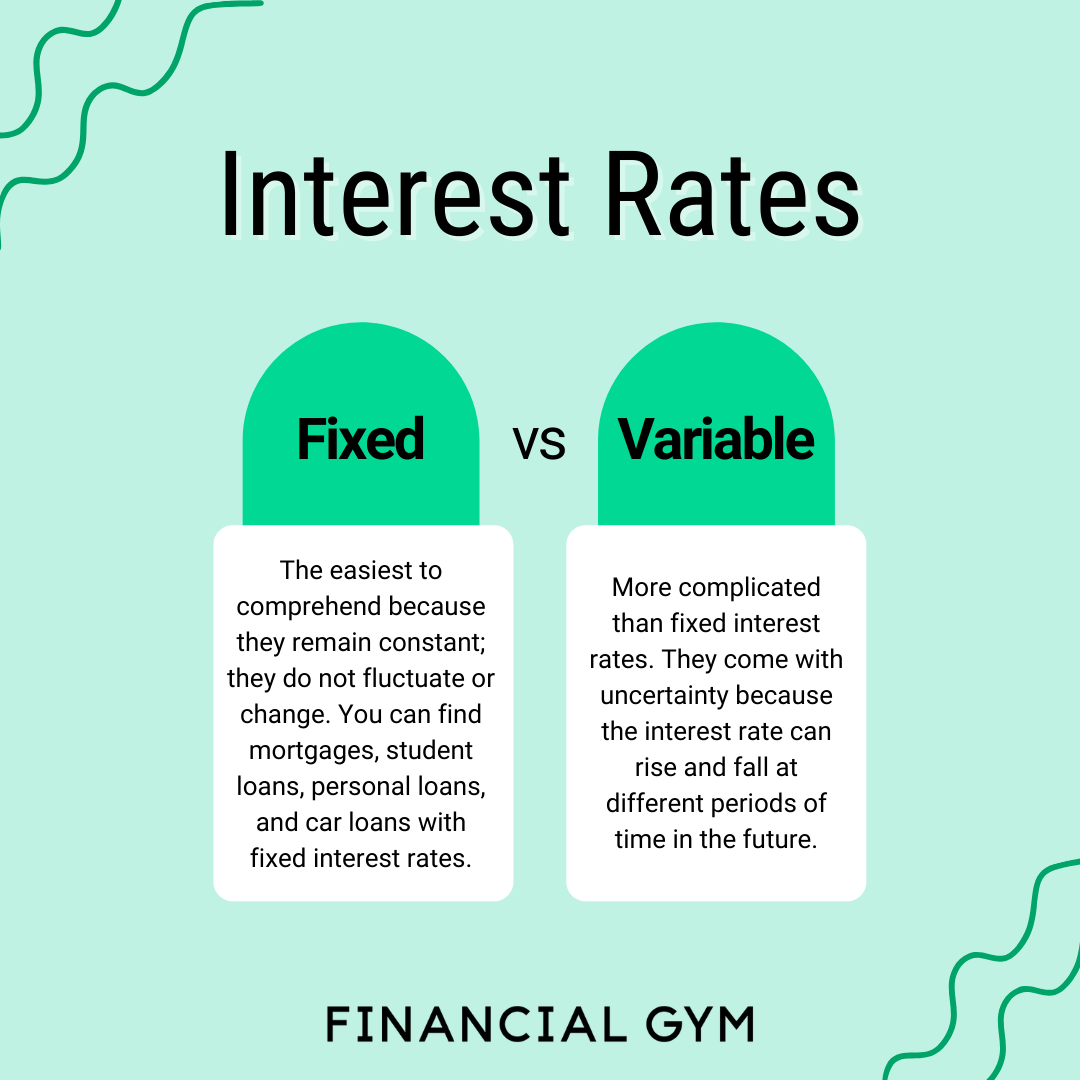
When it comes to loans, the interest rates can either be fixed or variable. Let’s break down the key differences between the two to help you understand which option might be better for you.
Fixed Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates remain the same throughout the life of the loan. This means that your monthly payments will also stay constant, providing predictability and stability. Even if market interest rates rise, your rate will not change, offering protection against potential increases.
Variable Interest Rates
On the other hand, variable interest rates can fluctuate based on market conditions. This means that your monthly payments may vary over time, potentially increasing or decreasing depending on the market rates. While initial rates may be lower than fixed rates, there is a risk of higher payments in the future if market rates rise.
Comparison of Fixed vs. Variable Rates
- Fixed rates offer stability and predictability, making budgeting easier.
- Variable rates can initially be lower but come with the risk of increasing payments in the future.
- Fixed rates protect against rising market rates, while variable rates offer the potential for lower payments if market rates decrease.
- Choosing between fixed and variable rates depends on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and market conditions.
Factors to consider when choosing between fixed and variable rates
When deciding between fixed and variable loan rates, there are several key factors to consider that can impact your financial situation. Let’s take a look at some of these factors below.
Identify financial goals that align with fixed rates
- Fixed rates provide stability and predictability, making it easier to budget for monthly payments.
- If you prefer the security of knowing exactly how much you need to pay each month, a fixed rate may be the best option for you.
- Fixed rates are ideal for long-term planning and for borrowers who want to avoid potential rate increases in the future.
Discuss the impact of economic conditions on variable rates
- Variable rates are directly affected by changes in the economy, such as fluctuations in the prime rate set by the Federal Reserve.
- During periods of economic growth, variable rates may increase, leading to higher monthly payments for borrowers.
- Conversely, in times of economic downturn, variable rates may decrease, providing savings for borrowers.
Provide examples of scenarios where each type of rate is beneficial
- For someone planning to stay in their home for a long time and wanting stable payments, a fixed rate mortgage would be a good choice.
- On the other hand, if a borrower plans to sell their home in a few years or expects interest rates to decrease, a variable rate mortgage might offer lower initial payments.
- Business owners who need flexibility in their loan terms might prefer a variable rate business loan to take advantage of potential rate decreases.
Risks associated with fixed and variable loan rates
When it comes to fixed and variable loan rates, there are different risks that borrowers need to be aware of. Let’s dive into the potential pitfalls associated with each type of rate.
Risks of Fixed Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates may provide stability and predictability in monthly payments, but they also come with risks. One of the main risks of fixed rates is that borrowers may end up paying more interest over time if market rates decrease. This means that you could miss out on potential savings if interest rates fall significantly.
Another risk of fixed interest rates is that borrowers may be locked into a higher rate if they want to refinance their loan. This could result in missed opportunities to take advantage of lower rates in the future.
To mitigate the risks associated with fixed interest rates, borrowers can consider shorter loan terms or opt for a hybrid loan that combines fixed and variable rates. Additionally, staying informed about market trends and refinancing options can help borrowers make informed decisions.
Market Conditions and Variable Rates
Variable interest rates are subject to changes in market conditions, which can lead to fluctuations in monthly payments. When market rates increase, borrowers with variable rates may see their payments rise, potentially causing financial strain.
On the flip side, when market rates decrease, borrowers with variable rates can benefit from lower monthly payments. However, this uncertainty can make budgeting more challenging and may result in higher overall interest payments over the life of the loan.
Strategies to Mitigate Risks
To mitigate the risks associated with variable rates, borrowers can consider refinancing to a fixed rate when interest rates are low. This can provide stability in monthly payments and protect against future rate hikes.
Another strategy is to set aside a financial buffer to cover potential payment increases if market rates rise. By planning ahead and being prepared for changes in interest rates, borrowers can better navigate the risks associated with variable rates.
Market trends influencing fixed and variable loan rates
The fluctuations in fixed and variable loan rates are heavily influenced by various market trends. Let’s take a closer look at how historical trends, factors contributing to rate fluctuations, and global events impact these rates.
Historical trends in fixed interest rates
Fixed interest rates have shown stability over the years, with lenders setting rates based on long-term market conditions. These rates are often tied to government bond yields and tend to remain constant throughout the loan term, providing borrowers with predictability and security in their payments.
Factors contributing to fluctuations in variable rates
Variable interest rates, on the other hand, are more susceptible to market changes. These rates are usually linked to a benchmark rate, such as the prime rate, and can fluctuate based on economic indicators, inflation rates, and the overall health of the economy. Borrowers opting for variable rates should be prepared for potential changes in their monthly payments.
Impact of global events on loan rates
Global events, such as geopolitical tensions, economic crises, or natural disasters, can have a significant impact on both fixed and variable loan rates. Uncertainty in the global market can lead to changes in interest rates as investors react to new information and adjust their expectations. Borrowers should stay informed about global events that could potentially affect their loan rates.
