Yo, ever wondered how to calculate ROI and make some serious cash? Buckle up as we dive into the world of ROI calculation with examples and tips that’ll have you feeling like a financial guru in no time.
Get ready to learn the ins and outs of ROI, from understanding the concept to interpreting results like a pro.
Understanding ROI Calculation
When it comes to ROI, it’s all about figuring out if something is worth the investment. ROI stands for Return on Investment, and it helps you determine how much profit or benefit you can get from a particular investment relative to its cost. In simple terms, it tells you if you’re getting bang for your buck.
To calculate ROI, you use a pretty straightforward formula:
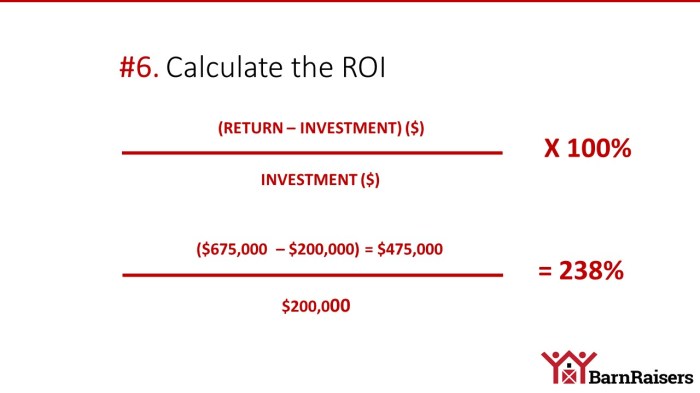
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100
This formula gives you a percentage that represents the return on your investment. The higher the percentage, the better the return.
Calculating ROI in Different Scenarios
- Scenario 1: You invest $1,000 in a stock and end up selling it for $1,200 after a year. Your ROI would be calculated as follows:
ROI = (($1,200 – $1,000) / $1,000) x 100 = 20%
Your ROI in this case would be 20%, indicating a 20% return on your initial investment.
- Scenario 2: You spend $500 on a marketing campaign that brings in $2,000 in revenue. To calculate the ROI:
ROI = (($2,000 – $500) / $500) x 100 = 300%
In this scenario, your ROI is 300%, showing that your marketing campaign generated a significant return on investment.
- Scenario 3: You buy a rental property for $200,000 and earn $20,000 in rental income per year. Calculating the ROI:
ROI = (($20,000 / $200,000) x 100 = 10%
With a 10% ROI, you can determine if the rental property is a profitable investment.
Components of ROI Calculation
When calculating ROI, there are key components that play a crucial role in determining the success and profitability of an investment. Each component contributes to the overall outcome and helps in making informed decisions.
Initial Investment
The initial investment is the amount of money put into a project, business, or venture. This includes all costs incurred to start or acquire the asset. The significance of the initial investment lies in its impact on the overall ROI. A higher initial investment may lead to a longer break-even point and lower ROI, while a lower initial investment can result in a quicker return and higher ROI.
Gain from Investment
The gain from the investment is the amount of profit or return generated from the initial investment. This can include revenue, earnings, or any other financial benefits obtained. The gain from the investment is essential in determining the success of the investment and calculating the ROI accurately. A higher gain from the investment leads to a higher ROI, while a lower gain results in a lower ROI.
Time Period
The time period refers to the duration over which the ROI is calculated. It is crucial in determining the efficiency and profitability of the investment. A longer time period may result in a lower ROI, as the gains are spread over a more extended period, while a shorter time period can lead to a higher ROI, as the returns are realized quickly.
Costs of Investment
The costs of investment include all expenses associated with maintaining and operating the investment. These can include operational costs, maintenance costs, and any other expenses incurred during the investment period. The costs of investment impact the overall ROI by reducing the net gain from the investment. Higher costs of investment lead to a lower ROI, while lower costs result in a higher ROI.
Risk Factors
Risk factors are uncertainties associated with the investment that may affect the expected returns. Understanding and evaluating risk factors is crucial in assessing the potential ROI and making informed decisions. Higher risk factors can lead to a lower ROI, as there is a higher chance of losses, while lower risk factors result in a higher ROI.
ROI Calculation Methods
When it comes to calculating ROI, there are different methods that can be used, ranging from simple to more advanced approaches. Each method has its own set of steps and is applicable in various real-life scenarios.
Simple ROI Calculation
- Simple ROI calculation involves dividing the net profit by the initial investment and multiplying the result by 100 to get a percentage.
- Formula:
ROI = (Net Profit / Initial Investment) x 100
- Example: Let’s say you invested $1,000 in a project and received a profit of $300. The simple ROI would be (300 / 1000) x 100 = 30%.
Advanced ROI Calculation
- Advanced ROI calculation takes into consideration factors like time value of money, risk, and opportunity costs.
- Formula:
ROI = (Net Present Value of Benefits – Net Present Value of Costs) / Net Present Value of Costs
- Example: If you are comparing two investment options with different timeframes and cash flows, the advanced ROI calculation would help you make a more informed decision.
Interpreting ROI Results
When it comes to interpreting ROI results, it’s all about understanding what the numbers are telling you. A positive ROI indicates that the investment has generated profit, while a negative ROI means that the investment resulted in a loss. A zero ROI suggests that the investment neither gained nor lost money.
Implications of Different ROI Values
- Positive ROI: A positive ROI is the goal of any investment. It shows that the investment was successful in generating profit. This means that for every dollar invested, you are getting back more than a dollar.
- Negative ROI: A negative ROI indicates that the investment did not generate enough profit to cover the costs. This could be a sign that the investment was not successful and adjustments need to be made.
- Zero ROI: A zero ROI means that the investment did not result in any profit or loss. While it’s not necessarily a bad thing, it also means that the investment did not generate any additional value.
Strategies for Optimizing ROI
- Identify areas for improvement: Analyze the factors that contributed to the ROI results and identify areas where adjustments can be made to increase profitability.
- Reduce costs: Look for ways to reduce costs without compromising the quality of the investment. This can help increase the overall ROI by improving the profit margin.
- Diversify investments: Consider diversifying your investments to spread risk and potentially increase the chances of achieving a positive ROI.
- Monitor and evaluate: Regularly monitor and evaluate the performance of your investments to identify trends and make informed decisions about optimizing ROI.
