So, like, loan interest rate calculation is no joke, right? It’s all about understanding how those interest rates can totally impact your loan repayments. Get ready to dive into this world of finance where numbers rule and knowledge is key.
Now, let’s break it down and see how loan interest rates work and why it’s crucial for borrowers to grasp these calculations.
Loan Interest Rate Calculation Overview
When you borrow money from a bank or a lender, they charge you an extra fee called interest. This interest is a percentage of the total amount you borrowed and is added to your loan repayment amount. Understanding how interest rates are calculated is crucial for borrowers to know how much they will end up paying back in total.
Impact of Interest Rates on Loan Repayments
Interest rates directly affect how much you pay back on a loan. The higher the interest rate, the more you will end up owing. For example, if you borrow $10,000 with a 10% interest rate, you will have to pay back $11,000 in total. However, if the interest rate is 5%, you would only need to repay $10,500.
Importance of Understanding Interest Rate Calculations
It’s essential for borrowers to grasp how interest rates work to make informed financial decisions. By understanding the calculations, you can compare loan offers, choose the best option, and avoid getting into debt traps. Knowing how much interest you will pay can also help you budget effectively and plan for future expenses.
Factors Affecting Loan Interest Rates
In understanding loan interest rates, it’s essential to grasp the key factors that play a role in determining them.
Credit Score
Your credit score is a significant factor in influencing the interest rate you are offered on a loan. Lenders use your credit score as a measure of your creditworthiness, with higher scores typically resulting in lower interest rates. Those with lower credit scores may face higher interest rates due to the perceived risk of lending to them.
Loan Term
The length of your loan term can also impact the interest rate you receive. Shorter loan terms generally come with lower interest rates compared to longer terms. This is because shorter terms pose less risk to the lender, leading to more favorable interest rates.
Loan Type
Different types of loans, such as fixed-rate and variable-rate loans, are affected differently by various factors. Fixed-rate loans have interest rates that remain constant throughout the loan term, offering predictability for borrowers. On the other hand, variable-rate loans have interest rates that can fluctuate based on market conditions, making them more unpredictable for borrowers.
Income and Debt-to-Income Ratio
Lenders also consider your income and debt-to-income ratio when determining the interest rate for a loan. A higher income and lower debt-to-income ratio can lead to lower interest rates, as they indicate a lower risk of default on the loan.
Market Conditions
External factors such as the state of the economy and market conditions can also influence loan interest rates. Changes in the economy, inflation rates, and the overall financial market can impact interest rates across different types of loans.
Methods of Calculating Loan Interest Rates
When it comes to calculating loan interest rates, there are specific formulas and methods that are commonly used. Understanding these calculations is essential for borrowers to know how much they will be paying in interest over the life of the loan.
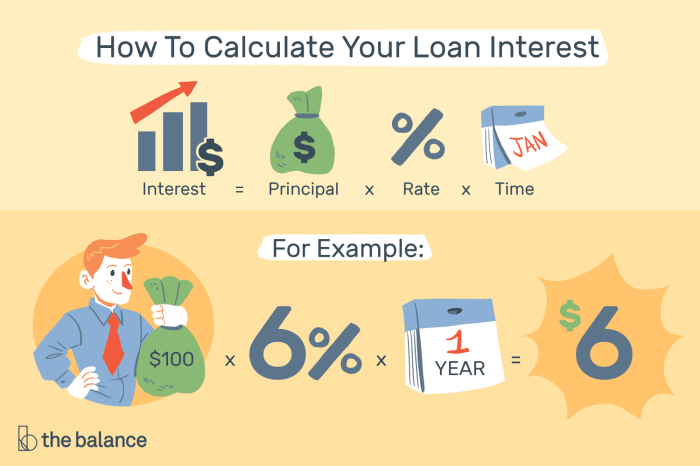
Simple Interest Calculation
To calculate simple interest on a loan, you can use the following formula:
Simple Interest = Principal x Rate x Time
- Principal: The initial amount of the loan.
- Rate: The annual interest rate expressed as a decimal.
- Time: The time period for which the loan is taken, typically in years.
Compound Interest Calculation
Calculating compound interest is a bit more complex than simple interest. The formula for compound interest is:
Compound Interest = Principal x (1 + Rate)^Time – Principal
- Principal: The initial loan amount.
- Rate: The annual interest rate as a decimal.
- Time: The number of compounding periods the interest is applied over.
Differences between Simple and Compound Interest
- Simple interest is calculated only on the principal amount, while compound interest takes into account both the principal and the accumulated interest.
- Simple interest remains constant throughout the loan term, whereas compound interest grows over time.
- With simple interest, the interest amount is the same each period, but with compound interest, the interest amount increases with each compounding period.
Importance of Understanding APR
Understanding APR (Annual Percentage Rate) is crucial when it comes to loan interest rate calculations. APR represents the total cost of borrowing, including not only the interest rate but also any additional fees or charges associated with the loan.
Difference Between APR and Nominal Interest Rates
When comparing APR to nominal interest rates, it’s essential to note that nominal rates only consider the interest charged on the loan amount. On the other hand, APR takes into account all costs associated with borrowing, providing a more accurate picture of the total expense.
- APR includes not only the interest rate but also any origination fees, points, and other charges.
- Unlike nominal rates, APR provides borrowers with a clear understanding of the true cost of borrowing.
Impact of APR on Total Cost of Borrowing
The APR directly impacts the total cost of borrowing, as it reflects the actual cost of the loan over its term. A higher APR means higher overall borrowing costs, even if the nominal interest rate seems low.
For example, a $10,000 loan with a 5% nominal interest rate but a 6% APR would cost more overall than a loan with a 5% nominal rate and a 5.5% APR due to additional fees included in the APR calculation.
