Yo, peeps! Let’s dive into the world of student loan interest rate calculation. Get ready to unlock the secrets behind how those interest rates are cooked up. It’s gonna be lit!
So, buckle up as we break down the nitty-gritty details about how student loan interest rates are calculated and what factors play a role in this whole money game.
Understanding Student Loan Interest Rate Calculation
When it comes to calculating student loan interest rates, there are a few key factors to consider. These rates determine how much you’ll end up paying back on top of the initial loan amount. Let’s break it down.
Factors Influencing Student Loan Interest Rates
- The type of loan: Different types of student loans, such as federal or private loans, come with varying interest rates. Federal loans typically have fixed rates set by the government, while private loans may have variable rates influenced by the market.
- Economic conditions: Overall economic conditions can impact interest rates. If the economy is doing well, interest rates may be higher, and vice versa.
- Credit history: Your credit score plays a significant role in determining the interest rate you qualify for. A higher credit score can lead to lower interest rates.
Types of Student Loan Interest Rate Calculations
Simple Interest Formula: Principal x Rate x Time = Interest
- Fixed Interest Rate: This type of rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan, making it easier to budget for consistent monthly payments.
- Variable Interest Rate: These rates can fluctuate based on market conditions, which means your monthly payments could change over time.
- Compound Interest Rate: In this calculation, interest is added to the principal amount, and future interest is calculated on the new total. This can lead to higher overall repayment amounts.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
When it comes to student loans, one of the key decisions borrowers need to make is whether to choose a fixed or variable interest rate. Let’s break down the differences between the two and understand the implications of each.
Fixed Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates on student loans remain the same throughout the life of the loan. Here are the pros and cons of opting for a fixed interest rate:
- Pros:
- Stability: With a fixed interest rate, borrowers know exactly how much they need to pay each month, making budgeting easier.
- Predictability: There are no surprises with fixed rates, as they do not fluctuate with market conditions.
- Peace of Mind: Borrowers are protected from sudden increases in interest rates, providing peace of mind.
- Cons:
- Potential Higher Initial Rates: Fixed rates may initially be higher than variable rates, which could result in higher overall costs over time.
- No Benefit from Decreases: Borrowers with fixed rates do not benefit from decreases in interest rates, missing out on potential savings.
Variable Interest Rates
Variable interest rates on student loans can change over time based on market conditions. Here’s how economic factors can impact variable interest rates:
Changes in the economy, such as fluctuations in the prime rate or inflation, can cause variable interest rates to increase or decrease.
- Impact of Economic Conditions:
- Rising Rates: If the economy is strong and interest rates increase, borrowers with variable rates may see higher monthly payments.
- Falling Rates: Conversely, during economic downturns or periods of low inflation, variable rates could decrease, leading to potential savings for borrowers.
- Risk of Uncertainty: Variable rates introduce an element of uncertainty, as borrowers may face unpredictable changes in their loan payments.
Formula for Calculating Student Loan Interest
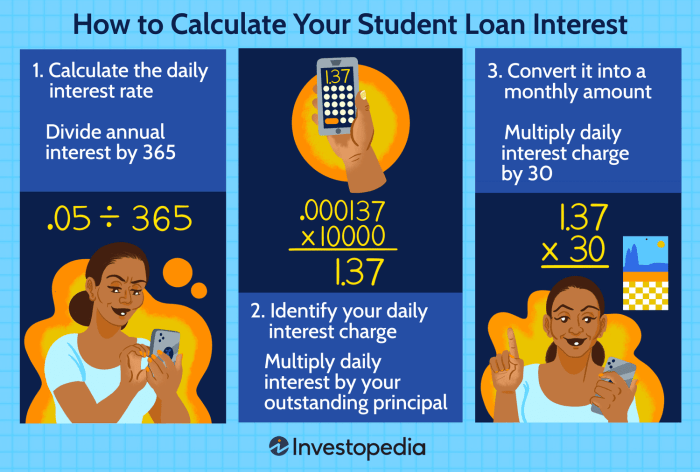
When it comes to understanding how student loan interest is calculated, it’s essential to know the formula that lenders use to determine the amount of interest you’ll pay over time. By having a clear grasp of this formula, you can better manage your loan repayment strategy and plan ahead effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Student Loan Interest
- Start by identifying the key components of the formula: the principal loan amount, the interest rate, and the time period over which interest is being calculated.
- Next, use the following formula to calculate the interest on your student loan:
Interest = Principal Loan Amount x Interest Rate x Time Period
- Plug in the values for each component into the formula. For example, if you have a principal loan amount of $10,000, an interest rate of 5%, and a loan term of 5 years, the calculation would be: Interest = $10,000 x 0.05 x 5.
- After calculating the interest, you can add this amount to the principal loan amount to determine the total amount you’ll repay over the loan term.
Examples of Applying the Formula
- Example 1: Principal Loan Amount = $15,000, Interest Rate = 4%, Time Period = 3 years
- Interest = $15,000 x 0.04 x 3 = $1,800
- Total Amount Repayable = $15,000 + $1,800 = $16,800
- Example 2: Principal Loan Amount = $20,000, Interest Rate = 6%, Time Period = 4 years
- Interest = $20,000 x 0.06 x 4 = $4,800
- Total Amount Repayable = $20,000 + $4,800 = $24,800
Importance of Understanding Interest Rate Calculation
Understanding how interest rates are calculated on student loans is crucial for students to make informed financial decisions. By knowing how interest accrues and compounds on their loans, students can better manage their debt and plan for repayment.
Not understanding interest rate calculations can have long-term financial implications for students. If students are unaware of how interest accumulates on their loans, they may end up paying significantly more over the life of the loan. This lack of understanding can lead to increased debt and financial strain in the future.
Tips for Managing Student Loans
- Regularly monitor your interest rates: Keep track of any changes in interest rates on your loans to anticipate how they will affect your monthly payments and total loan balance.
- Make extra payments towards the principal: By paying more than the minimum monthly payment, you can reduce the amount of interest that accrues over time and pay off your loan faster.
- Consider refinancing options: If you have high-interest rates on your loans, exploring refinancing options can help you secure a lower rate and save money on interest payments.
- Understand the impact of deferment or forbearance: While postponing loan payments can provide temporary relief, it’s important to understand how interest continues to accrue during these periods and the long-term implications on your total loan balance.
