Understanding stock options sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with american high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Get ready to dive into the world of stock options like never before as we explore the ins and outs of this fascinating financial instrument.
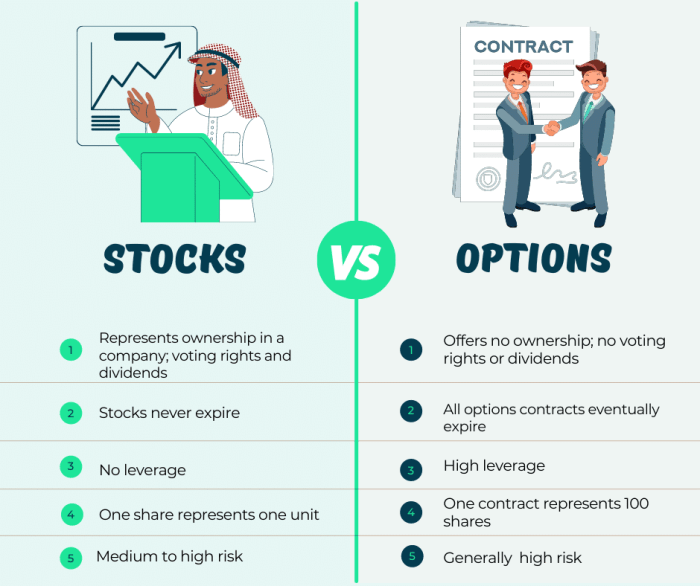
What are Stock Options?
Stock options are financial instruments that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific amount of a stock at a set price (strike price) within a certain period of time. Unlike buying stocks outright, stock options provide the opportunity to profit from price movements without actually owning the underlying stock.
Types of Stock Options
- Call Options: Call options give the holder the right to buy a stock at the strike price before the expiration date. If the stock price rises above the strike price, the call option holder can exercise the option and buy the stock at a discount.
- Put Options: Put options give the holder the right to sell a stock at the strike price before the expiration date. If the stock price falls below the strike price, the put option holder can exercise the option and sell the stock at a higher price, protecting against losses.
How Stock Options Work
Stock options can be used in various ways. For example, let’s say you believe that Company XYZ stock will increase in value. Instead of buying the stock outright, you can purchase a call option on Company XYZ. If the stock price rises as expected, you can exercise the call option and buy the stock at a lower price than the market value, profiting from the price difference. On the other hand, if the stock price does not increase as anticipated, you are not obligated to exercise the option and can let it expire, limiting your potential losses to the premium paid for the option.
Understanding Stock Option Terminology
When it comes to trading stock options, understanding key terms is crucial for making informed decisions and maximizing profitability. Let’s dive into some essential terminology that every trader should know.
Strike Price
The strike price is the price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset. It is the predetermined price at which the option contract can be exercised.
Expiration Date
The expiration date is the date by which the option contract must be exercised or it will expire worthless. It is essential to keep track of expiration dates to avoid losing the value of the option.
Premium
The premium is the price paid by the option buyer to the option seller for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset. It represents the cost of the option contract.
Intrinsic Value
The intrinsic value of an option is the difference between the current price of the underlying asset and the strike price. It indicates the real value of the option if it were to be exercised immediately.
Time Value
The time value of an option is the premium minus the intrinsic value. It represents the value attributed to the time left until expiration. As the expiration date approaches, the time value diminishes.
These terms play a crucial role in determining the value and profitability of stock options. Understanding how each term affects the pricing of options can help traders make informed decisions and manage risk effectively.
Benefits and Risks of Stock Options
Stock options offer investors a unique opportunity to potentially amplify their gains through leverage, diversify their portfolios, and hedge against market risks. However, along with these advantages come inherent risks that investors must carefully consider before engaging in stock options trading.
Advantages of Stock Options
- Leverage: Stock options allow investors to control a large amount of shares with a relatively small investment. This can amplify gains when the stock price moves in the desired direction.
- Diversification: By incorporating stock options into their investment strategies, investors can diversify their portfolios beyond traditional stocks and bonds, spreading risk across different assets.
- Hedging: Stock options can act as a form of insurance against potential losses in a stock position. Investors can use options to protect their portfolio from adverse market movements.
Risks of Stock Options Trading
- Limited Lifespan: Stock options have an expiration date, which means investors must be correct about the direction and timing of the stock price movement. If the option expires out of the money, it becomes worthless.
- Volatility: Options prices are influenced by factors like market volatility, time decay, and changes in interest rates. This volatility can lead to significant fluctuations in option prices.
- Complexity: Stock options involve intricate strategies and terminology that may be challenging for novice investors to grasp. Lack of understanding can result in significant losses.
How to Trade Stock Options
When it comes to trading stock options, it’s essential to understand the process of buying and selling these financial instruments. Factors like market conditions and volatility play a crucial role in determining the success of your trades. Here is a step-by-step guide for beginners on how to start trading stock options.
Opening a Brokerage Account
- Research and choose a reputable brokerage firm that offers options trading.
- Open a brokerage account and complete the necessary paperwork.
- Fund your account with the required minimum deposit to start trading.
Educate Yourself
- Learn the basics of stock options, including how they work and their potential risks and rewards.
- Understand different options trading strategies and how they can be used to achieve your financial goals.
- Stay updated on market news and trends that may impact the value of options.
Choosing the Right Options
- Decide whether you want to buy call options (betting on a price increase) or put options (betting on a price decrease).
- Select an expiration date and strike price that align with your trading strategy and expectations for the underlying stock.
- Consider the liquidity of the options you are trading to ensure you can easily enter and exit positions.
Executing Your Trades
- Place your options trades through your brokerage platform, specifying the type of order (market, limit, etc.)
- Monitor your trades closely and be prepared to adjust your positions based on market conditions.
- Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and protect your capital.
Strategies for Trading Stock Options
When it comes to trading stock options, there are several strategies that investors can use to maximize profits and minimize risks. These strategies include covered calls, protective puts, and straddles. Each strategy works differently and is most effective in specific market conditions.
Covered Calls
A covered call strategy involves selling a call option on a stock that you already own. This strategy allows you to generate income from the premium received for selling the call option. If the stock price remains below the strike price of the call option, you keep the premium and your stock. If the stock price rises above the strike price, you may have to sell your stock at the strike price.
Protective Puts
A protective put strategy involves buying a put option on a stock that you own. This strategy acts as insurance against a potential drop in the stock price. If the stock price falls, the put option will increase in value, offsetting the losses in the stock. If the stock price rises, you only lose the premium paid for the put option.
Straddles
A straddle strategy involves buying both a call option and a put option on the same stock with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy is used when investors expect a significant price movement in either direction but are unsure about the direction. If the stock price moves significantly in one direction, the investor profits from the corresponding option while limiting losses on the other option.
